Foundations of AI:
| Widget Connector | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Subtitle: "Exploring the Core of AI Technology"
Cover: Description: Dive into the essence of Artificial Intelligence with this comprehensive guide. Unravel the mysteries of neural networks, algorithms, and the digital brain. Whether you're a beginner or looking to deepen your knowledge, this book is your gateway to understanding the foundational principles that are shaping our future.
Outline: week 9/16 to 9/21
- Introduction to AI (Bobbi)
- History and Evolution of AI
- Understanding the Basics: Terminology and Concepts
- The AI Landscape: Types and Categories
...
Understanding the Basics: Terminology and Concepts
With the rise of Artificial Intelligence, many key terms are being used more frequently and often interchangeably. Before delving into the details, it's crucial to establish a clear understanding by defining these terms.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): The simulation of human intelligence by machines, especially computer systems, enabling tasks such as problem-solving, learning, and reasoning.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): A branch of AI focused on enabling machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. Example applications include speech recognition.
- Computer Vision (CV): A field of AI that focuses on enabling machines to interpret and understand visual information from the world, such as images and videos. It involves techniques to allow computers to extract meaningful data, recognize patterns, and make decisions based on visual input, mimicking human visual capabilities. Example applications include object detection and image classification.
- Machine Learning (ML): A subset of AI, focusing on the development of algorithms that allow machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming.
- Neural Networks (NN): NN is one type of ML algorithms. It is system of algorithms inspired by the human brain, consisting of layers of interconnected nodes (neurons) that process input data to generate outputs.
- Deep Learning (DL): A specialized subset of ML and NN that uses multiple layers of neural networks(deep neural networks) to model complex patterns in large datasets.
The following are some key definitions that are commonly used in AI:
- Supervised Learning: A type of machine learning where the model is trained on labeled data, learning to map inputs to outputs.
- Classification: A type of supervised learning in ML where the goal is to assign input data to predefined categories or labels. A model is trained on labeled data to predict the category of new, unseen data based on learned patterns.
- Regression: Another type of supervised learning where the task is to predict continuous numerical values based on input data. It models the relationship between the input variables (features) and a continuous output variable.
- Unsupervised Learning: Involves training a model on unlabeled data, allowing it to identify patterns or groupings without explicit instructions.
- Reinforcement Learning: A learning paradigm where an agent learns by interacting with an environment, receiving feedback in the form of rewards or penalties.
The AI Landscape: Types and Categories
Understanding AI technologies helps companies choose the right tools for their needs and smoothly integrate them into their current operations.
(working on the diagram)
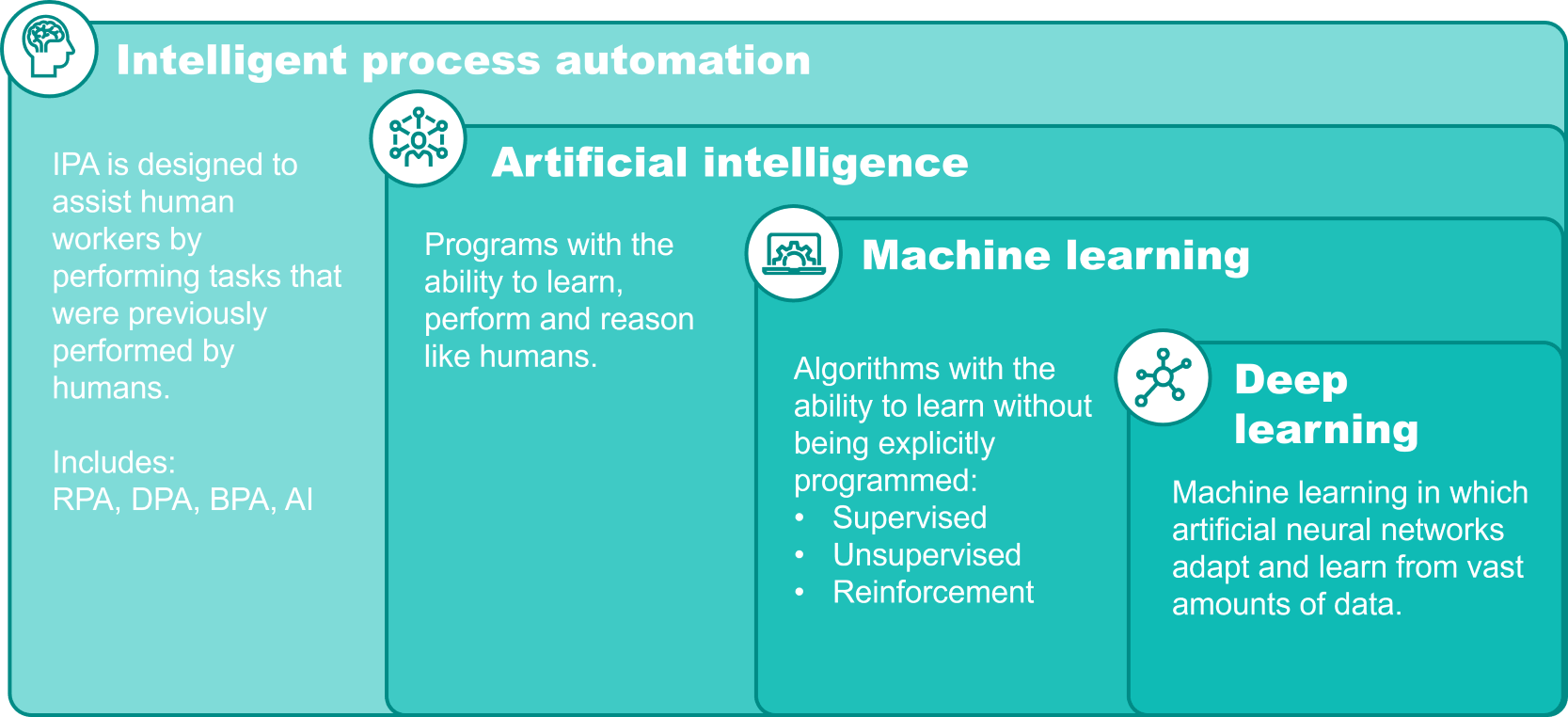
AI technologies can be viewed as a set of nested, layered tools, all part of the broader category called IPA (Intelligent Process Automation).
Intelligent process automation
IPA is a grouping of technologies used to manage and automate digital processes and is designed to assist human workers by augmenting human labor and performing tasks that are typically repetitive processes. IPA includes the following technologies:
- Robotic process automation (RPA): Seeks to automate tasks within existing processes
- Digital process automation (DPA): Uses low-code tools to automate processes that can span multiple applications with a focus on automating or partially automating tasks involved in a variety of business practices that typically require some form of human interaction
- Business process automation (BPA): Seeks to automate and streamline multi-step processes
- AI: Systems with the ability to learn, perform, and reason like a human
Moving into the AI realm, IPA begins to make decisions based on the provided data and identified trends to augment human decisions or even make decisions independently. IPA utilizes AI to drive innovation and optimize and streamline workforce efficiency.
Artificial intelligence
AI is an overarching term that encompasses the field of developing computer systems to perform tasks that require human intelligence, such as reasoning, decision-making, and pattern learning and includes any technology that falls within the scope of ML and automation.
Additional subfields of AI include:
- Natural language processing (NLP): Seeks to enable machines to understand, interpret, and respond to human language in a valuable way
- Large language model: Trained on extensive datasets to understand and generate human-like text and can perform various language-related tasks
- Computer vision: Seeks to enable computers to derive information from images, videos, and other data
- Deep learning: ML in which multi-layer artificial neural networks adapt and learn from vast amounts of data
With the continued advancements in autonomous vehicles and the ability to tackle complex, nuanced challenges, artificial intelligence continues to evolve, inching closer to human-like cognitive abilities.
Machine learning
Machine Learning (ML) enables AI systems to learn from data by recognizing patterns and making predictions or recommendations based on statistical analysis. It can adapt over time to new data, but its learning is generally guided by specific features and rules defined by developers.
There are four types of ML:
- Supervised learning: In supervised learning, models are trained on labeled data. Each training example is paired with an output label. The algorithm iteratively makes predictions on the training data and is corrected by the teacher, allowing the model to learn over time.
- Unsupervised learning: Machine learning models that operate without the need for labeled data. Unlike supervised learning where models are trained on a labeled dataset, unsupervised learning algorithms work with datasets that have not been annotated or categorized. Unsupervised learning is crucial in scenarios where obtaining labeled data is impractical or too expensive. It provides a method to extract meaningful information and insights from raw, unstructured data, paving the way for deeper understanding and better decision-making.
- Semi-Supervised Learning: Semi-supervised learning falls between supervised learning and unsupervised learning. In semi-supervised learning, the algorithm is trained on a dataset that contains both labeled and unlabeled data. Generally, a small amount of data is labeled while a large amount of data is unlabeled.
- Reinforcement learning: When the model learns from its actions and feedback from the environment, such as a robot navigating a maze or a game agent playing chess, before using an algorithm to find a policy that maximizes a reward function intending to learn optimal behavior for complex and dynamic situations.
ML is widely used in various applications, such as speech recognition, image recognition, spam filtering, fraud detection, and self-driving cars.
Deep learning
Deep learning is a subset of ML that uses artificial neural networks to enable digital systems to learn and make decisions based on unstructured, unlabeled data. A neural network is a series of algorithms that can learn from input data to discern features, such as distinguishing characteristics among various images, to make independent decisions without explicit programming.
ML enables AI systems to learn from data by recognizing patterns and making predictions or recommendations based on statistical analysis. It can adapt over time to new data, but its learning is generally guided by specific features and rules defined by developers.
On the other hand, deep learning employs neural networks with multiple layers (hence why it's often referred to as deep) to analyze various factors of data. Unlike traditional ML, deep learning autonomously extracts features from raw data, eliminating the need for manual feature extraction. It learns from data in a way that is somewhat analogous to human learning, through a hierarchy of concepts where each layer of the network extracts and refines features from the input data.
Generative models, like those used in generative adversarial networks (GANs), are a notable application of deep learning. They learn to generate new data that resembles the training data and can be used to improve decision-making capabilities over time as they are exposed to more data. However, it's not just generative AI that benefits from deep learning; other forms of AI, like those used in image and speech recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems also leverage deep learning to enhance their performance and capabilities over time.
Generative AI
Generative AI refers to a category of algorithms that are capable of generating new data that resembles a given set of training data. While it's not exclusively about language models, it indeed encompasses them. These algorithms can create a variety of content types including images, text, computer code, or audio based on the patterns they learn from the input data, aiding in accelerating the creative process.
Large language models like ChatGPT are instances of Generative AI applied to text generation. They are trained on vast datasets to produce human-like text based on the input prompts they receive. These models can be fine-tuned to perform a myriad of tasks, enhancing their versatility and utility across different domains.
It's important to note that generative AI also includes models like GANs and variational autoencoders (VAEs) which are used for generating images, audio and other types of data beyond text. Hence, while large language models are a subset of generative AI, the term generative AI encompasses a broader range of models and capabilities.
Generative AI has evolved into an advanced search and content generation tool integrated across various industries to augment daily tasks and produce new content. With 55% of organizations piloting or in production mode with generative AI [1], the growth of AI in the market highlights the need for risk management as the creation of new AI-driven content accompanies inherent risks.
(Tripur i found this newsletter and thought it might be useful:
https://a.tldrnewsletter.com/web-version?ep=1&lc=e12d7e94-184d-11ef-a642-8f5f787eab04&p=703435f8-799a-11ef-8b11-371f32244928&pt=campaign&t=1727098081&s=08e00d007f71dd28628b374f6ad56d10faf70f8bccb1a24f7d28d634eb2752f8)