1. Introduction
...
- Hyperledger Fabric
- Token
- DAO
- New Consensus Mechanism
The
...
span of a Governance, Risk
...
and Compliance
...
- Third-Party Risk Management
- Environmental Social Governance (ESG)
- Cyber Risk Management
- Compliance Management
- Internal and IT audit
- Regulatory Change Management
- Enterprise & Operational Risk Management
- Data Protection and Privacy
The areas of GRC on the blockchain are still on their nascent stage and waiting for the right time to explode as the internet did back then. To expand some of the use cases of GRC on the blockchain.
Audit Processes:
Audits can be categorized into various forms like security audits, financial auditor compliance, and regulatory audit. In the traditional audit processes, audits like account reconciliations, trial balances, supporting Evidence are provided to the auditor by the Business or Auditees in a variety of electronic and manual formats where it will require significant time to invest while planning for an audit. This Evidence provides an assurance that a long tedious audit process is being performed in accordance with the auditing standards. Instead, in the blockchain network, the auditors can have real-time access to the data by having read-only nodes on the blockchain network. A traditional monthly process can be reduced and simplified to a day’s process by implementing audit processes on the blockchain. This will also ensure that the Audit trail of Evidence is managed with the participants in a transparent manner.
Third-Party Risk Management:
When an organization onboarding the third party, the company needs to be extra cautious and be aware of the bad history if any. That will save the organization from reputational risk. A survey questionnaire can be floated to a third party and the responses can be recorded on the blockchain which cannot be tampered with by any other third party. That will give more visibility about the risk score of the third-party organization which can be evaluated by the organization and decide whether to onboard them or not.
Regulatory Change Management:
There’s an ever-changing regulatory environment that organizations have to comply with and adhere to. Regulatory changes are mandated by the regulatory authorities. A lot of times, the entire process of complying with regulatory standards becomes time-consuming while doing it in a traditional way. However, all the information about the processes that need to be compliant with can be deployed on the blockchain, so the audit process will be simple and easy. Regulatory standards can be deployed on the blockchain so that the data will always be accessible and untampered. Some of the regulatory standards are:
- For Healthcare and Insurance – HIPPA – Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996
- For IT sector – ISO – International Organization for Standardization
- For IT sector and Cross-sector – NIST – National Institute of Standards and Technology
- For Privacy – GDPR – General Data Protection Regulation (EU based standards)
- For BFSI – AML – Anti-Money Laundering; KYC – Know Your Customer
- For BFSI and Cross-Sector – PCI-DSS – Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards
- For Enterprise Fraud Control – SOX – Sarbanes Oxley
Other Important Aspects:
Transparency in compliance can bring trust in the company and anyone associated with the company can ensure the company will do all the right things for the business.
Auditing of new technology adoption by enterprises has been a key challenge for Auditors, it is essential to know if the PoCs and standards are right to meet the organization's goals to get digitally transformed.
ESG ensures the whole supply chain right from financial funding to Carbon footprint to Social causes like philosophy and gender equality are governed in the right way so that Enterprise can be transparent about practices, showcase the right certificates, partner with 3rd parties that adhere to ESG norms to bring trust within and outside the organization
...
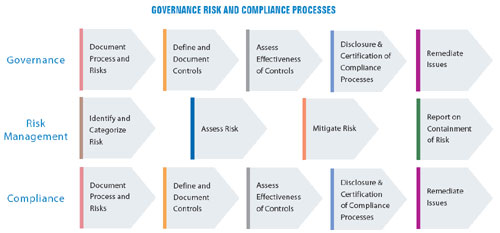
process includes three elements
- Governance is the oversight role and the process by which companies manage and mitigate business risks
- Risk management enables an organization to evaluate all relevant business and regulatory risks and controls and monitor mitigation actions in a structured manner
- Compliance ensures that an organization has the processes and internal controls to meet the requirements imposed by governmental bodies, regulators, industry mandates, or internal policies.
Governance: With an increase in activism among shareholders and increased scrutiny from the regulatory bodies, corporate boards and executive teams are more focused on governance-related issues than ever before. The governance process within n organization includes elements such as definition and communication of corporate control, key policies, enterprise risk management, regulatory and compliance management and oversight (e.g., compliance with ethics and options compliance as well as overall oversight of regulatory issues) and evaluating business performance through balanced scorecards, risk scorecards, and operational dashboards. A governance process integrates all these elements into a coherent process to drive corporate governance.
Risk Management: With the recent jump in regulatory mandates and increasingly activist shareholders, many organizations have become sensitized to identifying and managing areas of risk in their business: whether it is financial, operational, IT, brand, or reputation-related risk. These risks are no longer considered the sole responsibility of specialists - executives and the boards demand visibility into exposure and status so they can effectively manage the organization’s long-term strategies. As a result, companies are looking to systemically identify, measure, prioritize and respond to all types of risk in the business, and then manage any exposure accordingly. A risk management process provides a strategic orientation for companies of all sizes in all geographies with a formal process to identify, measure and manage risk.
Compliance: An initiative to comply with a regulation typically begins as a project as companies race to meet deadlines to comply with that regulation. These projects consume significant resources as meeting the deadline becomes the most important objective. However, compliance is not a one-time event - organizations realize that they need to make it into a repeatable process, so that they can continue to sustain compliance with that regulation at a lower cost than for the first deadline. When an organization is dealing with multiple regulations at the same time, a streamlined process of managing compliance with each of these initiatives is critical, or else, costs can spiral out of control, and the risk of non-compliance increases. The compliance process enables organizations to make compliance repeatable and hence enables them to sustain it on an ongoing basis at a lower cost.
Note: GRC Framework definition by MetricStream
1.1. Mission
The Governance Risk and Compliance Special Interest Group (GRCSIG ) represents industry professionals working together to study how Hyperledger DLTs interact with Governance Risk & Compliance use cases. The Mission of this group is to research blockchain as a technology and its right use in the GRC space, work with other contributors to define standards in the GRC space and work on PoCs to generate value and to develop acceptance of DLT with GRC Practitioners. If interested and open to contributing, you can register yourself via this link, you will need a Linux Foundation ID to access the SIG. You can add your detail to the Member Directory post-registration. please also Subscribe to the Group Mailing List and post an introduction there so other group members can get to know you.
...
Hyperledger SIGs are open and global communities where anyone from anywhere can and should be able to participate, contribute, and access tools and information. For example, this means that even with meetings that are held via teleconference, we have to involve those not on the calls who are online. Best practice in an open and global community is to keep in mind time zone differences of the group participants and make sure to include non-meeting participants in group discussions and decisions by active use of the mailing list, the wiki and Rocket Chat. All SIGs must adhere to the Hyperledger Code of Conduct and Anti-Trust Policy (see below) during meetings:
...
GRCSIG membership shall be free and open to members of the community who have an interest in issues as they relate to the SIG topic technologies in general, and blockchain technologies. SIG membership is established by subscription to the mailing list.
All participation in the groups activities is voluntary. It is perfectly fine to listen in to a group and do nothing. Of course active contribution is our goal, but it is not a requirement for membership.
Anyone can propose agenda items, activities, and work products. In work products, the only requirement is there's enough buy-in from community members to want to volunteer to complete the product.
7.2 Governance
Governance of the GRCSIG shall be managed through its membership in accordance with the guidelines and overriding jurisdiction of Hyperledger leadership.
...
Facilitating the group and helping ensure that the mission statement and goals are observed and met
Scheduling and facilitating regular General Meetings open to all GRCSIG membership
Developing and distributing meeting agendas at least one business day before the scheduled meeting
Ensuring that all group members have the opportunity to participate in decisions and provide input even when not attending a meeting. SIG communities are global and a chair should make efforts to ensure all are included in the community’s activities. This can be done by ensuring meeting notes are shared after calls and any major decisions are shared on the mailing list.
Ensure recordings/minutes are taken during meetings which captures the discussion and includes a list of meeting participants, shared post meeting, and are added to the SIG wiki page
Manage the SIG wiki page
Generate Special Interest Group Quarterly Updates to present to Hyperledger POC in a timely manner and communicate regularly on any concerns or questions related to the SIG
Serving as a proxy and ambassador for GRCSIG membership (as appropriate)
Enforcing adherence to the Hyperledger Code of Conduct and communicating the Anti-Trust Policy
...
All GRCSIG membership meetings are placed on the Hyperledger Community Calendar. To ensure that a cancelled meeting is removed from the calendar, the person leading the meeting shall send a meeting cancellation request to zoom@hyperledger.org.
Additionally, a meeting cancellation notification shall be made to GRCSIG membership through both the mailing list and chat channels.
...